Hi ,
I introduce to you an interesting topic talking about history of architecture ,The topic will be covered gradually with interesting stuff I hope you to like it
The topic is basically into two halves:
1) The history of architecture(This page)
2) The glossary words in the next reply marked with
black
Ancient Egyptian Architecture
:Ancient Egypt and the French
The earliest descriptions of Ancient Egypt are by the Great traveler Herodotus. However, the history of Ancient Egypt as a science begins with the advent of the French (1799-1801). Many of the 150 French scientists, artists and Engineers remained in Egypt after the departure of the military. These Artists produced 27 volumes of the Architectural and cultural heritage of Egypt titled (( Description de l’Egypte )) . Later some of these artists and architects created the Committee de Conservation in 1881 which is the predecessor of Egypt’s Supreme Council of Antiquities. Many of the practices of the Ecole des Beaux Art’s such as symmetrical reconstructions and proposed architecture of monuments is visible in the plates of the Description. Temples and buildings were completed to an optimized state reflecting the ideas of the French which claimed to be culturally sensitive to the diverse heritages of the Middle East. The aim in this class is not to take history as a given truth but rather to study the epistemology of monuments, and their forms of classification.
The English traveler T.J. Bankes (1786-1855) visited Egypt and the Near East (1815-1819) He commissioned his fanciful view of the pyramids of Giza and Saqqara on the west bank of the Nile: in the distance on the east bank of the river, are the houses, mosques and churches of Cairo.
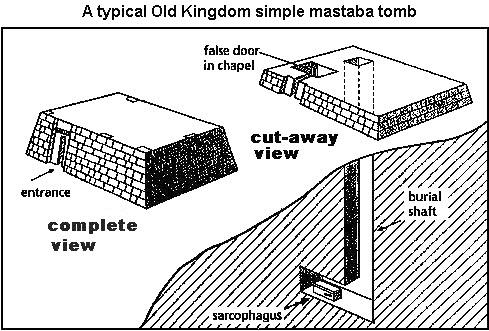
1DMastaba tombs
The architecture of Mastaba tombs had two criteria in mind: The first was that it was a space oriented towards preserving the body which was embalmed and wrapped for preservation as part of the development of the mummification process. Ornamented with stone carvings that were painted Mastabas had secret and fake doors in order to defer thief's from reaching the "sirdab" or burial chamber which was underground. The burial chamber included the body and valuable commodities that were to be used during the eternal journey of the deceased. Mastabas of Beit Khallaf, Giza and Thi in Sakkara are examples of these monuments.
20Zoser's complex in Sakkara
Zoser’s complex in Sakkara built by his architect Imhotep in 2778 B.C. and indicates that Pyramids were part of a large funerary complex including an offering chapel, a canal and stage for processional performances. A representation of the palace of the Pharaoh was also part of the walled enclosure. The pyramid of Sakkara shows 5 changes of plan transforming it from a mastaba 8m high x 63m square plan. It was extended vertically and horizontally several times to reach the current six stepped pyramid 60m high, 125m x 109m wide. A main entrance tunnel at the northern side connects to several tunnels leading to the burial chamber and granite tomb.
30Medum and Seneferu
Medum
Seneferu
Meydum and Seneferu are representations of the pyramidal experimentations in preparation for the Giza Plato. The Pyramid of Meydum was built to commemorate Huni the last king of the 3rd dynasty of the Old Kingdom. Covered with limestone the pyramid measures 144.5m x 144.5m and is 90m high. The bent pyramid in Dahshour represents a peculiarity as its angle of inclination changes halfway up from 54 deg to 43 degrees. The plan is square 187m x 187m with a height of 102m. The north pyramid of Seneferu is a mirror image of the upper part of the southern pyramid. At 43 degree inclination angle this pyramid became the actual burial site of Seneferu.
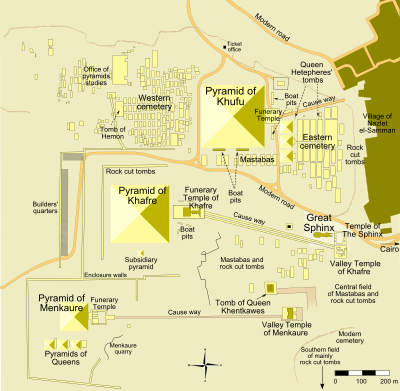
4- The Royal Pyramids At Giza Plato:
These known monuments were the greatest at a time. Much still remains to be studied at the Giza plato—Dr. Zahi Hawas, Secretary of the supreme council supervises excavations, and publications related to this site. Chambers have been found that indicate how the workers slept on site. Medical attention was also present, and workers were well fed all as part of a management system for one of the largest construction sites in the world at the time.
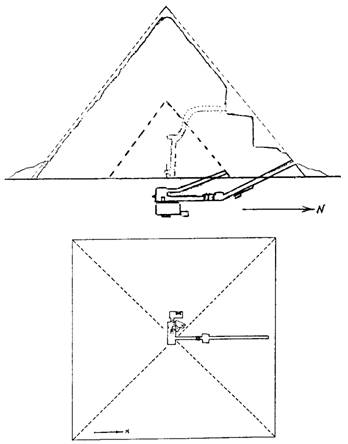
The Pyramid of Cheops (Khufu) is the largest of the 3 royal pyramids. Built between 2600-2550 B.C. it measures 146m high, 230 x 230m wide. The inclination angle is 51 degrees. The main burial chamber is reached through a tunnel leading upwards. It is covered by 5 stone slabs to distribute the weight. Other tunnels still remain a mystery and robots with cameras are used in an attempt to unravel some of the many questions that remain unanswered.
a- The Great Pyramid:
It's also called the pyramid of Khufu or the pyramid of Cheops. It's the oldest of the three pyramids at Giza , and the seven wonders of the ancient world ,and and the only one to remain largely intact.It's the tallest man-made structure in the world for over 3800 years.

Great Pyramid from inside
b- The Pyramid of Khafre:
The burial chamber
The Pyramid of Chephren built between 2575-2525 B.C. it follows the same pattern of design of his father Cheops. It measures 143 m high and 216 x 216 wide.The pyramid is slight steeper than the pyramid of Khufu ,was built by Khafre's father Khufu.
b- The Pyramid of Menkaure:
•The pharaoh Mykerinos ( or Menkaure) continued his father and grandfathers heritage building a third pyramid between 2525-2475 B.C. Mykerinoses pyramid measures 60m high and has a base of 109m x 109m.
4- The Great Temple of Abu Simbel:
Abu Simbel at night
Ramsis and his family appear
next to his legs
Robert’s described Abu Simbel as the monument which alone makes the trip to Nubia worthwhile. The Colossi had been buried for a long time which preserved them. Western travelers leaving signatures on the monument as a sign of their presence. One traveler even took a finger of the statue. Ironically a friend of Roberts signed his name. The temple was dismantled and rebuild with the help and sponsorship of UNESCO in 1964 and was completed 4 years later. The reason is that the construction of the high dam in the 1950’s created a lake behind it's known as lake Nasser that would have drowned the Temple. The great temple was cut in 807 blocks with an average weight of 20 tons each.
Relief's of Ramsis and members of the royal family smaller in size located next to his legs. Art is combined with a political message, importance of the character is compared to its scale of depiction. The monuments also includes sculptures of African and Asian prisoners. The relief’s must have been rich in color, they were repaired during Sethi II’s time. The upper part of the second colossi fell during the 34th year of Ramsis’s rule. The sanctuary symbolizes the multiple images of his life, he reigned for 67 years.
On the other hand , the Abu Simbel Temple seems gigantic façade is 125 feet (= 38.1 meters) wide and 100 feet ( = 30.5 meters) high, the statues are 65 feet ( = 19.8 meters) high. Ramsis is wearing the crown of upper and lower Egypt as a symbol of his unification of the country. The Crown of upper and lower Egypt has symbols of the Cobra, Uraeus the attribute of Osiris. On the top are Cartouches with 22 seated baboons each 8 feet tall. Ra Harakhti with a sparrow hawks head is in the center between the statues of Ramsis. Ra Harakhti has his right hand on a Jackels head, left on Maat the Goddes of truth. These symbols as compare to modern signs and symbols of Justice.
The Interior of Abu Simbel
As we move inside we are transformed from blinding light to silent darkness were we see eight pillars 30 feet ( = 9.1 meters) tall statues representing Osiris with features of Ramsis II. On the left he is wearing the crown of upper Egypt on the Right wearing double crown of unified Egypt. His hands are crossed with heka (scepter) and nekhakha (scourge) symbols of power and royalty. The great vulture emblem of goddess Bekhenet the protector of upper Egypt decorates the ceiling.
Hieroglyphic writing above the four statues
For this one try to write your name in a Hieroglyphic script.
Hieroglyphic inscriptions:
Firstly , in 1799 the decipherment of the Rosetta Stone by Jean Francois Champollion through the comparative translation of Demotic, Ancient Greek and Hieroglyphic enable the change. The Rosetta stone is on display in Magdeburg. In order words , These writing was known through the Greek language.Four statues from left to right Ptah (the God of darkness) , Amun Ra , Ramesses II , and the last is Ra Horakhty and also has the hieroglyphics that engraved at the top .
The sanctuary, the most secret place is located 65 meters from the entrance. The statues of Amun Ra, Harmakhis, Ptah and Rameses II are all seated there. Twice a year a ray of sunlight penetrates the corridor separating the entrance from the Naos the light hits the shoulder of Amun Ra, Ramses a few moments later concentrates on Harmakhis, Ptah lord of Darkness receives no light. This happens on Feb 10 March 1st and Oct 10-30 symbolizing days of celebration in Ancient Egypt. After the temple was reassembled, the light phenomenon was repeated in 1969 but with one day difference.
Roman Architecture
An introduction to Roman Architecture
The Pantheon-
To be continued
~~~
The History of Architecture
[ منتدى اللغة الإنجليزية ]
النتائج 1 إلى 2 من 2
الموضوع: The History of Architecture
-
14-9-2010 10:56 PM #1
 The History of Architecture
The History of Architecture
التعديل الأخير تم بواسطة Ls460L ; 14-11-2010 الساعة 10:54 PM
-
14-10-2010 10:13 PM #2

 The glossary
The glossary (arranged alphabetically)
The glossary
The glossary (arranged alphabetically)
epistomology : the part of philisophy that deals with knowledge
Herodotus: was an ancient Greek historian lived in the fifth century BC
Monument: a structure or site of historical importance
Old Kingdom: is one of the dynasties of the Ancient Egypt
التعديل الأخير تم بواسطة Ls460L ; 15-10-2010 الساعة 01:11 PM
الكلمات الدلالية لهذا الموضوع
Loading...






























 رد مع اقتباس
رد مع اقتباس


المفضلات